It is important to take good care of an open wound to prevent infections and promote healing. Good wound care is necessary for both a small and a large open wound. In this article you will learn what an open wound is and how you can treat it step by step.
What is an open wound?
An open wound is a wound where the skin and possibly underlying tissue is exposed. This type of wound can range from small and superficial to deep and severe. The wound can range from a graze to a cut. It is also possible that you have a wound that was deliberately left open due to a medical procedure.
There are different types of open wounds:
- Abrasions: These are caused by rubbing against a rough surface and are often superficial, but can be painful and sensitive. There is also a risk of infection.
- Lacerations: These wounds are mainly caused by a sharp object and can be deep or superficial.
- Stab wounds: These are deep wounds caused by a pointed object, such as a nail or knife. Stab wounds have a high risk of infection.
- Lacerations: These are caused by a forceful impact or pulling motion that tears the skin and tissues. These wounds can have unusual shapes.
- Surgical open wound: it is possible that a wound is deliberately left open after an operation. Closing this wound may have involved a risk of infection. You should always seek advice from a doctor before treating a surgical open wound.
How to care for an open wound
To prevent infection and promote healing, you should take good care of an open wound. Follow these steps to properly treat an open wound:
Wound assessment:
Inspect the wound carefully, paying attention to the size, depth, and amount of blood coming from the wound. Also check for dirt in the wound. For serious wounds, such as deep or heavily bleeding wounds, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Cleaning the wound:
Gently clean the wound with clean water, physiological saline or disinfectant to remove dirt and bacteria. Use a sterile gauze to dab the wound clean, avoid rubbing as this can damage the tissue.
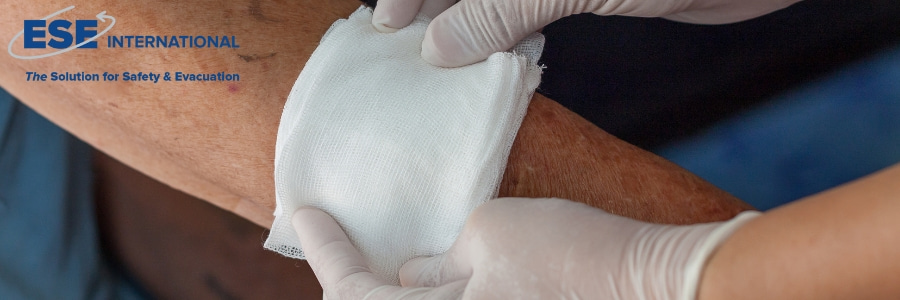
Covering the wound:
Cover the wound with a sterile, non-stick dressing to protect the wound from dirt and grime. For smaller wounds, a plaster may be sufficient, while for larger or deeper wounds, a wound compress or gauze is needed, which you then secure with a bandage .
Caring for the wound:
Change the dressing regularly, depending on the severity of the wound and the amount of wound fluid. Keep the wound clean and dry and ensure that the wound is not unnecessarily exposed to dirt or fluid.
Materials needed to care for an open wound:
- Physiological saline solution or clean water
- Sterile gauze
- Non-adherent wound compress
- Plaster or bandage
- Bandage
- Clean hands or sterile gloves
Important: If the wound is bleeding heavily, is very deep, or if there is dirt or other foreign objects that cannot be easily removed, contact a medical professional immediately.
Aftercare of open wound
Aftercare is important to ensure that the wound heals properly. Check the wound daily for signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, pus formation or warm skin.
Change the dressing when necessary and ensure that the wound remains clean and dry. If the wound shows signs of infection or does not heal properly, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Open wound won’t heal?
If an open wound does not heal properly, this may have several causes:
- Infection: An infection can delay the healing process and should be treated immediately. In this case, consult a medical professional.
- Insufficient blood flow: Poor blood circulation can limit the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the wound, which slows healing.
- Chronic conditions: Conditions such as diabetes can affect the recovery process because they often weaken the immune system and reduce blood supply.
- Unhealthy lifestyle: Smoking and drinking can slow down the healing process of wounds.
The healing process of an open wound occurs in several stages: inflammation, tissue formation, and maturation. If your wound still does not heal after a few weeks or if complications arise, it is important to consult a medical professional.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical attention. In case of serious injuries or doubts, consult a qualified first responder. In case of serious injuries, call 112 or go to the doctor immediately.